
- +86-13363869198
- weimiaohb@126.com

Dec . 06, 2024 01:21 Back to list
Phenacetin Powder CAS 62-44-2 Supplier for Pharmaceutical Applications and Quality Assurance
Exploring Phenacitin Powder CAS No. 62-44-2
Phenacitin, a compound with the chemical formula C9H11N3O2, is known in the scientific community primarily for its applications in the fields of pharmacology and biochemistry. With the CAS number 62-44-2, this substance has attracted attention due to its various industrial uses, particularly in the production of other chemicals and pharmaceuticals. This article delves into the properties, applications, manufacturing processes, and safety considerations associated with phenacitin powder, highlighting its relevance in contemporary industries.
Properties of Phenacitin
Phenacitin is characterized by its white crystalline powder form, which is soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol and acetone but exhibits limited solubility in water. Its molecular structure includes an acetamide group, contributing to its chemical reactivity and interactions. The melting point of phenacitin is approximately 137 to 140 degrees Celsius, indicating its stability under room temperature conditions. These properties render phenacitin suitable for various applications, particularly in conformance to the stringent requirements of pharmaceutical production.
Applications in Industry
Phenacitin has found several significant applications across various industries, most notably in pharmaceuticals. Historically, it has been used as an analgesic (pain-reliever) and antipyretic (fever-reducer) drug. However, due to concerns over potential toxicity and adverse effects, its use in human medicine has ebbed in favor of safer alternatives.
In contemporary applications, phenacitin is also a vital intermediate in the synthesis of dyes, agricultural chemicals, and other organic compounds. Its ability to participate in various chemical reactions makes it a valuable building block in the formulation of complex molecules. Furthermore, phenacitin is sometimes utilized in laboratory settings for research purposes, such as pathophysiological studies or to better understand drug interactions.
Manufacturing Processes
phenacitin powder cas 62-44-2 factory
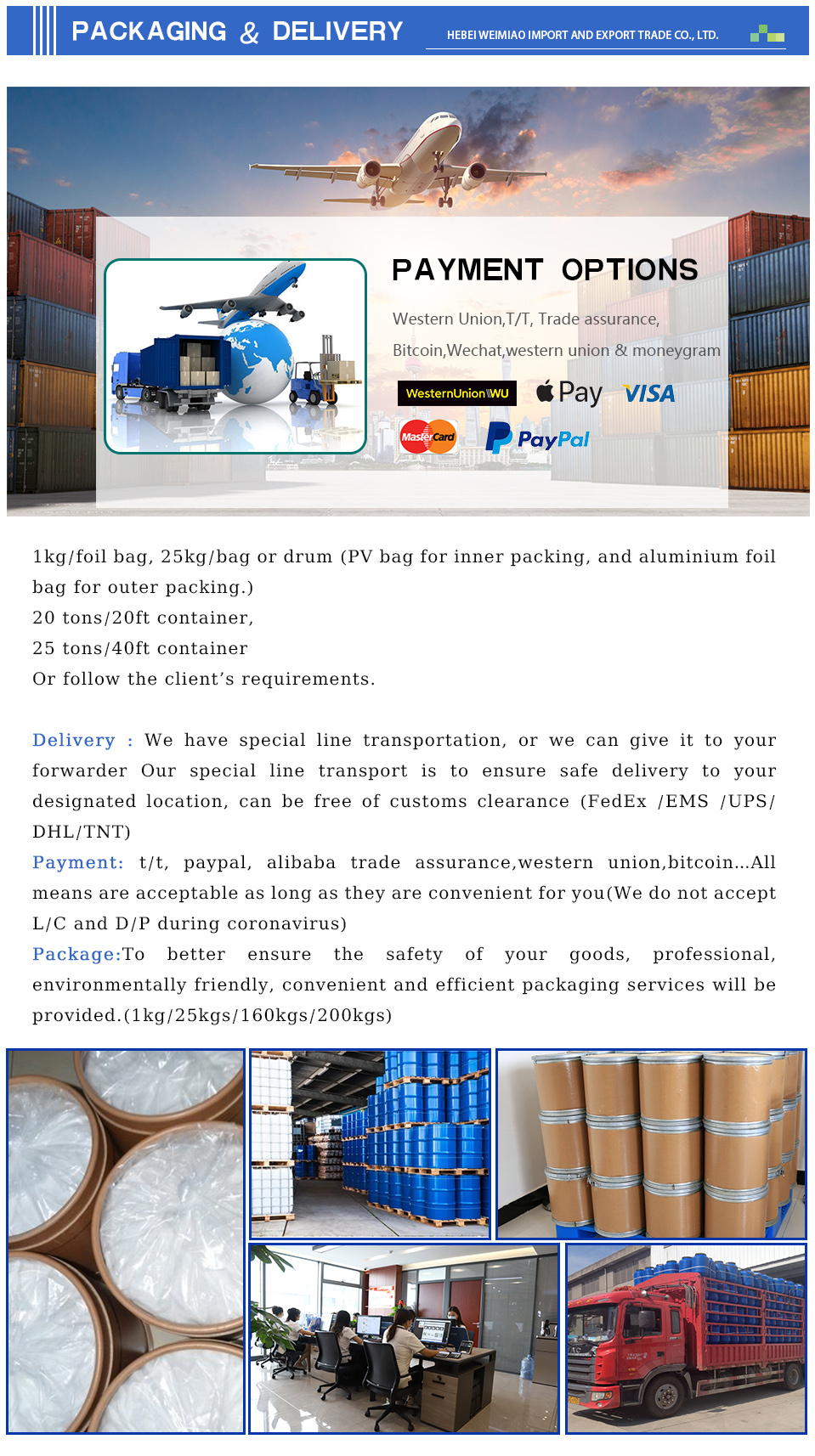
The production of phenacitin powder involves specific chemical reactions. Manufacturers typically synthesize it through the reaction of 4-aminophenol with acetic anhydride or acetyl chloride. This acetylation process yields the desired phenacitin compound, which can then be purified to obtain a high-quality powder form. Quality control during manufacturing is essential to ensure that the final product meets regulatory standards and is safe for intended uses.
Given the shift towards environmentally friendly practices, some manufacturers are exploring greener synthesis methods, including the use of alternative solvents and reagents. This not only reduces waste but also mitigates potential hazards associated with chemical processes.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations
As with many chemicals, safety is paramount when handling phenacitin. Workers involved in its production must adhere to strict guidelines set forth by regulatory bodies to mitigate exposure risks. Personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and respiratory protection is recommended to minimize inhalation or skin contact.
Additionally, phenacitin is subject to regulatory scrutiny regarding its environmental impact. Manufacturers are responsible for proper waste disposal and ensuring that by-products do not pose a risk to ecosystems. Compliance with local and international regulations is crucial for manufacturers to operate sustainably.
Conclusion
In summary, phenacitin powder (CAS No. 62-44-2) is an important compound with diverse applications primarily in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries. While its historical uses have diminished, its role in synthesis and research continues to be significant. With ongoing advancements in manufacturing techniques and a focus on safety and environmental impact, the future of phenacitin looks promising. As industries evolve, so too will the methods and applications of this compound, ensuring its relevance for years to come.
-
Top CAS: 79099-07-3 Factories & Wholesale Supplier from China
NewsJul.30,2025
-
High-Quality GS-441524 for White Liquid Type Factories & Suppliers
NewsJul.29,2025
-
High-Quality Pharmaceutical Intermediates for Sale – Reliable Supply
NewsJul.29,2025
-
High-Quality Pharmaceutical Intermediates for Sale - Reliable Solutions
NewsJul.29,2025
-
High-Quality Pharmaceutical Intermediates Supplier for Global Market
NewsJul.28,2025
-
GS-441524 for White Liquid Type Factories – High Purity & Reliable Supply
NewsJul.28,2025