
- +86-13363869198
- weimiaohb@126.com

Oct . 18, 2024 08:48 Back to list
pharmaceutical formulation intermediates
Pharmaceutical Formulation Intermediates Key Components in Drug Development
Pharmaceutical formulation intermediates play a critical role in the development of effective and safe medications. These intermediates are substances that are used in the formulation process of drugs, serving as building blocks that contribute to the drug's stability, efficacy, and release characteristics. The science of drug formulation is complex, involving various disciplines such as chemistry, biology, and engineering. Understanding the significance and types of formulation intermediates is essential for the pharmaceutical industry.
At the heart of pharmaceutical formulation intermediates are excipients, which are inactive substances that serve various functions in drug formulations. Excipients can include fillers, binders, disintegrants, preservatives, and stabilizers, each contributing to the overall effectiveness of the drug product. For instance, fillers like lactose or microcrystalline cellulose help to create a suitable volume for tablet formulations, ensuring consistency and aiding in the production process.
The selection of appropriate excipients is critical, as they can influence the drug’s bioavailability—the extent and rate at which the active ingredient or active moiety is absorbed and becomes available at the site of action. Poorly chosen intermediates can lead to challenges in drug solubility or stability, ultimately hindering the therapeutic effectiveness of the drug. Thus, understanding the interaction between excipients and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) is vital for formulators aiming to optimize drug performance.
pharmaceutical formulation intermediates
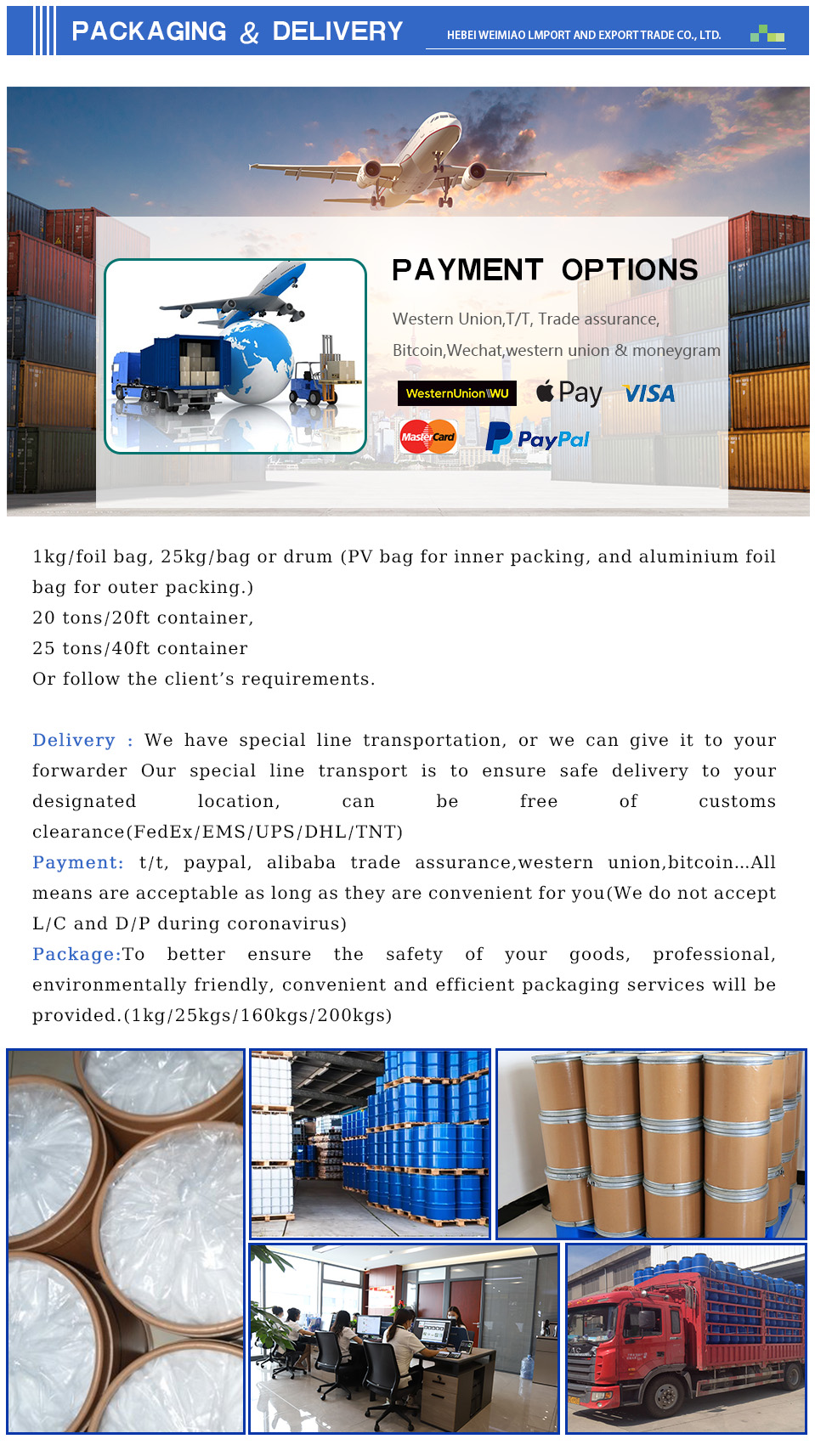
Moreover, the process of formulating drugs often involves the development of various intermediate compounds. For instance, in the process of creating a solid dosage form, intermediates such as granules or pellets may be produced. These forms undergo various tests to ensure that they meet the stringent regulations imposed by health authorities. The transition from raw materials to final drug product is a significant part of pharmaceutical research and development.
Stability is another crucial aspect of formulation intermediates. Many drugs are sensitive to environmental factors, such as heat, moisture, and light. Therefore, formulators must utilize intermediates that help to protect the active ingredients from degradation. Using stabilizing agents or encapsulation techniques can enhance the stability of the drugs over their intended shelf life, ensuring that patients receive effective medication throughout the product’s use.
The regulatory landscape around pharmaceutical formulation intermediates is also evolving. With increased scrutiny on drug quality and efficacy, manufacturers must ensure compliance with good manufacturing practices (GMP) and other regulatory guidelines. This means that pharmaceutical companies must invest in research and development to find innovative intermediates that not only enhance drug delivery but also meet regulatory requirements.
In conclusion, pharmaceutical formulation intermediates are integral to the successful development of drugs. From excipients that support the drug’s delivery to intermediates that enhance stability and performance, these components are foundational to achieving the desired therapeutic outcomes. As the pharmaceutical industry continuously evolves, the importance of understanding and optimizing these intermediates remains paramount, paving the way for the next generation of safe and effective medications. As new technologies emerge, the potential for innovation in this field is boundless, promising a brighter future for drug formulation and patient care.
-
GS-441524 for White Liquid Factories: Boost Efficiency & Purity
NewsAug.04,2025
-
Premium Pharma Intermediates | AI-Optimized Synthesis
NewsAug.03,2025
-
GS-441524 White Liquid Production for Factories | AI-Optimized
NewsAug.02,2025
-
AI-Optimized CAS: 79099-07-3 Factories for High Yield
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Premium CAS 1451-83-8 Factory with GPT-4 Turbo | AI-Optimized
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates - AI-Optimized Synthesis & Purity
NewsJul.31,2025