- +86-13363869198
- weimiaohb@126.com

May . 14, 2024 11:12 Back to list
Intermediates Pharma Market Trends: A guide for smarter sourcing
Intermediates Pharma Market Trends: A guide for smarter sourcing
An overview of the Intermediates manufacturing category for pharmaceutical procurement teams. This guide provides you with the overall market size and trends, key drivers, opportunities and challenges, contract manufacturers in the category and advice on how to improve strategic supplier partnerships.
Definition
Intermediates refer to chemical compounds that are used as building blocks or precursor materials in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) or finished pharmaceutical products.
These intermediates play a crucial role in the pharmaceutical industry by enabling the efficient and cost-effective production of drugs.
Pharmaceutical intermediates can include various organic and inorganic compounds, such as reagents, catalysts, chiral compounds, and other functional groups, which are utilised at different stages of the drug manufacturing process.
Pharmaceutical intermediates serve as a critical link between the discovery of new drug candidates and the commercial production of pharmaceutical products. They allow for the synthesis of complex molecules and provide the necessary chemical transformations to convert raw materials into active drugs.
Pharmaceutical intermediates contribute to enhancing drug efficacy, stability, and bioavailability, thereby ensuring the quality and effectiveness of medications. These intermediates also play a vital role in achieving regulatory compliance by meeting the stringent standards set by regulatory authorities.
GLP-1 Medication Semaglutide Tirzepatide Weight Loss Peptides CAS: 2023788-19-2
Market Size and Trends
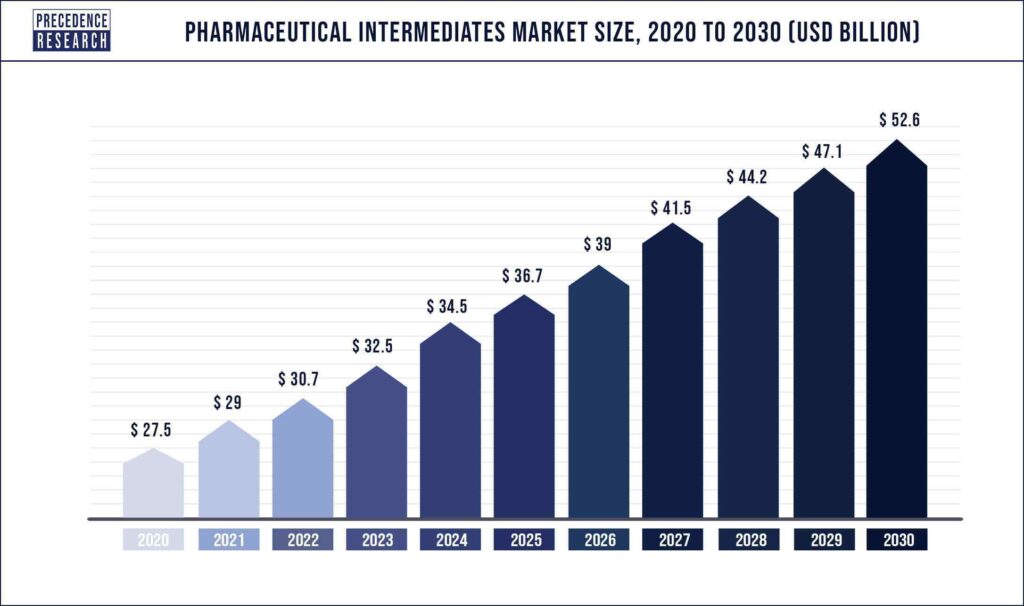
The global pharmaceutical intermediates market was valued at USD 29 billion in 2021 and is expected to grow to over USD 52.6 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 6.3% from 2021 to 2030.
This growth can be attributed to several factors, including the increasing demand for generic drugs, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and the expansion of pharmaceutical manufacturing activities in emerging markets.
The market growth is also driven by advancements in drug development and the need for efficient and cost-effective production processes. Pharmaceutical intermediates play a crucial role in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and the manufacturing of finished pharmaceutical products. These intermediates serve as building blocks and precursor materials, enabling the transformation of raw materials into complex molecules required for drug production.
Categories of Pharmaceutical Intermediates
The pharmaceutical intermediate market can be broadly categorized into three main categories based on their chemical structures, functional groups, and applications in drug synthesis:
1. Reagents and Catalysts
Reagents and catalysts are essential components in various chemical reactions involved in the synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates.
They facilitate the conversion of starting materials into desired intermediates, promoting reaction efficiency and selectivity.
Examples of reagents and catalysts include acids, bases, oxidizing agents, reducing agents, and transition metal catalysts.
2. Chiral Compounds
Chiral compounds are molecules that possess asymmetry, existing in two mirror-image forms (enantiomers).
They are of great importance in the pharmaceutical industry due to their ability to interact differently with biological systems.
Chiral intermediates are widely used in the synthesis of chiral drugs, enhancing their therapeutic efficacy and reducing side effects.
3. Functional Group Intermediates
Functional group intermediates consist of specific chemical functional groups, such as amines, alcohols, esters, and halides.
These intermediates serve as key building blocks for the introduction or modification of specific functional groups in drug molecules.
They enable the incorporation of desired properties, such as improved solubility, stability, or target specificity, into pharmaceutical compounds.
Note: these categories are not mutually exclusive, and pharmaceutical intermediates often belong to multiple categories depending on their chemical composition and usage
Market drivers for Pharmaceutical Intermediates
The pharmaceutical intermediate market is influenced by various trends that shape its growth and dynamics.
Key trends include:
- Technological Advancements: Advances in synthetic chemistry, process optimization, and automation have led to more efficient and sustainable methods for producing pharmaceutical intermediates.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stringent regulatory requirements for drug manufacturing and quality control drive the demand for high-quality intermediates that comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other regulatory standards.
- Outsourcing and Contract Manufacturing: Increasingly, pharmaceutical companies are outsourcing intermediate manufacturing to contract manufacturers, enabling cost savings, access to specialized expertise, and flexibility in production capacity.
- Sustainability Practices: The industry is increasingly adopting sustainable practices in intermediate production, such as green chemistry principles, waste reduction, and the use of environmentally friendly solvents and reagents.
These trends have a significant impact on the development and production of pharmaceutical intermediates, influencing the strategies adopted by manufacturers and contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs).
-
158861 67 7: Premium Peptides for Weight & Fat Loss
NewsAug.08,2025
-
Quality Pharma Intermediates & API | Leading Manufacturer
NewsAug.07,2025
-
GHRP-2 (158861 67 7) Peptides for Fat & Muscle Gain
NewsAug.06,2025
-
GS-441524 for White Liquid Factories: Boost Efficiency & Purity
NewsAug.04,2025
-
Premium Pharma Intermediates | AI-Optimized Synthesis
NewsAug.03,2025
-
GS-441524 White Liquid Production for Factories | AI-Optimized
NewsAug.02,2025