
- +86-13363869198
- weimiaohb@126.com

Yan . 13, 2025 10:04 Back to list
100% safe delivery SGT-151 SGT-163 SGT-78 with best price
Exploring the World of DMT (CAS 120-61-6) An In-Depth Guide for Conscious Seekers
Trustworthiness in addressing DMT's properties and usages is paramount, especially given its powerful psychoactive nature and legal status in many regions. As the interest in psychedelic substances grows, ensuring accurate information dissemination is critical. This includes understanding appropriate dosing, environmental settings for consumption, and recognizing the importance of guidance from trained professionals. Among researchers and users, there is a consensus that DMT experiences should be approached with respect and caution due to the intensity of its effects. From an authoritative standpoint, extensive ethnobotanical studies reveal DMT's historical significance, particularly in indigenous cultures where it has been ritually consumed as a part of traditional shamanic practices. These cultures perceive DMT as a sacred element that facilitates communication with spiritual realms and provides insights into the collective unconscious. Such historical contexts enrich the modern discourse on DMT, suggesting that its role extends into the metaphysical domain. Innovation in DMT research continues to grow, with technological advancements allowing for more controlled and replicable studies. By synthesizing DMT in regulated environments, scientists can precisely manipulate variables to evaluate its effects, safety profile, and potential therapeutic avenues. This transformative research is galvanizing a shift in public perception and academic interest, potentially paving the way for DMT to become a mainstream component of mental health frameworks pending further comprehensive studies. Finally, the discourse surrounding DMT must adhere to ethical considerations, ensuring that any potential commercialization emphasizes accessibility, safety, and scientific integrity. By fostering collaboration between neuroscientists, clinicians, and ethicists, the potential of DMT can be harnessed responsibly within the framework of contemporary science and society. Navigating the complexities of DMT will ultimately contribute to a broader understanding of human consciousness, psychological well-being, and the enduring quest for understanding our place within the universe.
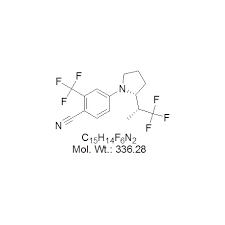

Trustworthiness in addressing DMT's properties and usages is paramount, especially given its powerful psychoactive nature and legal status in many regions. As the interest in psychedelic substances grows, ensuring accurate information dissemination is critical. This includes understanding appropriate dosing, environmental settings for consumption, and recognizing the importance of guidance from trained professionals. Among researchers and users, there is a consensus that DMT experiences should be approached with respect and caution due to the intensity of its effects. From an authoritative standpoint, extensive ethnobotanical studies reveal DMT's historical significance, particularly in indigenous cultures where it has been ritually consumed as a part of traditional shamanic practices. These cultures perceive DMT as a sacred element that facilitates communication with spiritual realms and provides insights into the collective unconscious. Such historical contexts enrich the modern discourse on DMT, suggesting that its role extends into the metaphysical domain. Innovation in DMT research continues to grow, with technological advancements allowing for more controlled and replicable studies. By synthesizing DMT in regulated environments, scientists can precisely manipulate variables to evaluate its effects, safety profile, and potential therapeutic avenues. This transformative research is galvanizing a shift in public perception and academic interest, potentially paving the way for DMT to become a mainstream component of mental health frameworks pending further comprehensive studies. Finally, the discourse surrounding DMT must adhere to ethical considerations, ensuring that any potential commercialization emphasizes accessibility, safety, and scientific integrity. By fostering collaboration between neuroscientists, clinicians, and ethicists, the potential of DMT can be harnessed responsibly within the framework of contemporary science and society. Navigating the complexities of DMT will ultimately contribute to a broader understanding of human consciousness, psychological well-being, and the enduring quest for understanding our place within the universe.
Latest news
-
China CAS: 79099-07-3 Factories | High-Purity Bulk Supply
NewsAug.27,2025
-
High-Purity Pharma Intermediates & API | Reliable Supply
NewsAug.26,2025
-
High-Quality Pharma Intermediates | Trusted Manufacturer
NewsAug.25,2025
-
Premium Pharma Intermediates & API | Trusted Global Supplier
NewsAug.24,2025
-
High-Purity cas 1451-83-8 Factory | LGD-3303 & GHRP-6 Supplier
NewsAug.23,2025
-
Wholesale CAS: 79099-07-3 Factories - China Pharma Grade
NewsAug.22,2025